Study shows payback times for heat pumps could plunge by 2030 – pv magazine International
McKinsey & Firm says in a brand new report that payback intervals for warmth pumps might fall by as much as 38% by 2030.
By 2030, the payback interval for warmth pumps and rooftop photo voltaic could fall to intervals of a number of years, in keeping with a brand new report by McKinsey & Firm.
“The attractiveness of every funding (as measured by the payback interval) is more likely to enhance as EU industries scale and cut back manufacturing and set up prices,” stated the worldwide administration consulting agency.
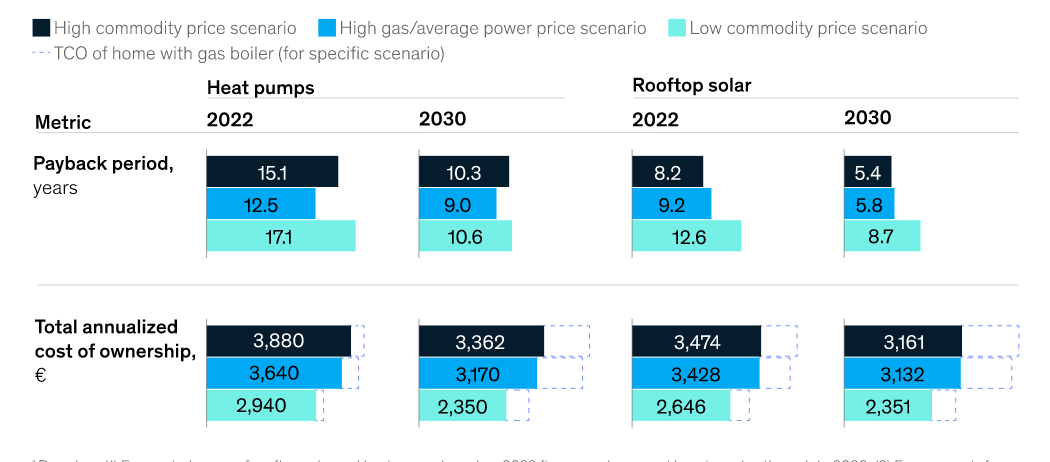
The evaluation considers three worth situations, utilizing a German single-family home for example. A “excessive commodity worth” state of affairs, a “excessive fuel however common electrical energy worth” state of affairs, and a low commodity worth state of affairs, the place fuel costs return to historic averages and electrical energy costs have reached new lows.
Warmth pumps and rooftop photo voltaic each have the longest payback intervals within the low electrical energy worth state of affairs, however additionally they have the longest payback intervals between 2022 and 2030. The payback intervals for warmth pump could fall by 38%, from 17.1 years in 2022. to 10.6 years in 2030. The payback interval for rooftop photo voltaic could fall by 31%, from 12.6 years in 2022 to eight.7 years in 2030 .
Warmth pumps have the shortest payback interval beneath the “common electrical energy worth” state of affairs. The payback interval could be lowered by 28% throughout this era. For rooftop photo voltaic, common payback intervals might fall from 9.2 years in 2022 to five.8 years in 2030.
Rooftop photo voltaic has the shortest payback interval beneath the “high-power worth” state of affairs. It might fall by 34% from 8.2 years in 2022 to five.4 years in 2030. The payback interval for warmth pumps could go from 15.1 years in 2022 to 10.3 years in 2030, down 32%.
“These payback intervals (and subsequently family power prices) could be lowered as a consequence of lowered electrical energy prices because the electrical energy system decarbonises and decentralises (discount of peak prices) hours),” says McKinsey & Firm.
The brand new examine focuses on three initiatives which might be reported to have the best potential to enhance the power effectivity of EU buildings: the ramping up of photo voltaic and warmth pump installations on the roof, and the advance of insulation in buildings.
It discovered that annual rooftop photo voltaic deployment would should be near 33 GW to fulfill the EU’s Match-for-55 and Repower EU targets, in comparison with a report fee of twenty-two GW by 2022 and a mean of 10 GW within the final 4 years.
“Warmth pump deployment should additionally proceed to develop at 12.5% a 12 months till 2030 to succeed in the RePowerEU goal of 54 million warmth pumps by 2030,” say the authors. By the top of 2021, Europe is reported to have put in 15 million warmth pumps, with McKinsey estimating a further 2.5 million installations by 2022.
The consultancy agency proposes 5 key drivers to assist promote these modifications: growing the workforce, organising applicable incentive mechanisms, attracting financing and personal capital, investing in grid infrastructure, and create net-zero and round provide chains.
The upcoming March version of the pv journal reveals an prolonged article from the McKinsey report creator in regards to the outlook and competitiveness of the European photo voltaic manufacturing business.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].