Perovskite solar cell with 25.3% efficiency via new ligand – pv magazine International
A Chinese language analysis group has designed a perovskite photo voltaic cell with a brand new ligand generally known as 3-amidinopyridine. These molecules are reported to have the ability to successfully cut back anion emptiness defects, thus making certain increased energy conversion effectivity and distinctive stability.
Researchers at Shaanxi Regular College in China have designed a novel management technique to cut back the formation of anion emptiness defects in halide perovskite photo voltaic cells and located that this new methodology ends in increased effectivity. and extraordinary energy.
The brand new methodology, which they describe as a one-stone-two-birds technique, makes use of a ligand generally known as 3-amidinopyridine (3AP) to pin the anions to the system. Anions can management the nucleation and progress of perovskite crystals and act as a passivating agent to enhance crystallinity, thus making certain higher effectivity.
The scientists declare that the 3AP molecules deposited within the perovskite layer are in a position to type a powerful chemical bond with the lead(II) iodide (Pb–I) interlayer of the cell and, because of this, create a long-lasting impact on pinning.
“We discovered that the 3AP molecules are organized parallel and anti-symmetrically between the Pb-I frameworks with a brief interlayer distance of three.45 angstrom(Å), which is shorter than that obtained for beforehand reported ligands, resulting in uncommon coordination inside the crystals,” they defined.
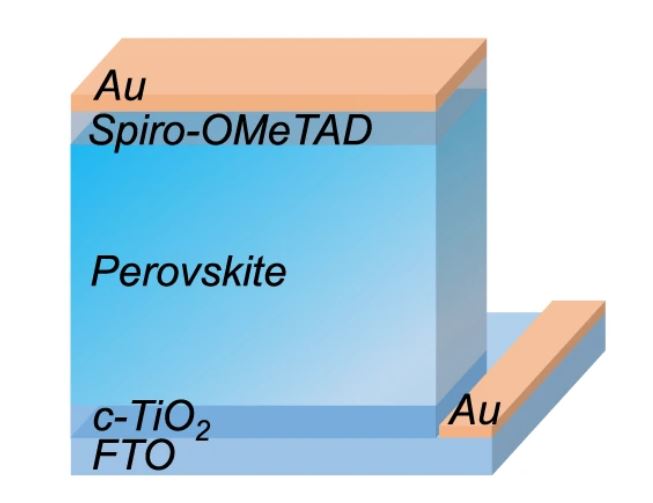
The researchers constructed the cell with a substrate product of tin oxide (FTO), a titanium oxide (TiO2) electron transport layer, a halide perovskite generally known as α-formamidinium lead iodide generally known as α-FAPbI3, a spiro-OMeTAD gap transport layer, and gold (Au) steel contacts.
They evaluated the efficiency of the system via density practical concept (DFT) calculations and in contrast it to a reference cell that makes use of generally used giant natural ligands akin to 2-phenethylammonium (PEA) and n-butylammonium (BA).
The group discovered that the 3AP-based cell achieved a most energy conversion effectivity of 25.3%, open-circuit voltage of 1.181 V, short-circuit present of 26.04 mA cm.-2, and a fill issue of 82.21%. The reference cell with out 3AP molecules reached an effectivity of twenty-two.76%, open-circuit voltage of 1.123 V, short-circuit present of 24.94 mA cm.-2and a fill issue of 81%.
Via additional measurements, the teachers additionally ascertained {that a} 3AP-based cell with out encapsulation was in a position to retain 92% of its preliminary effectivity after 5000 h publicity to ambient circumstances. “Anion-vacancy defect engineering via sturdy molecule-perovskite coordination gives an efficient and easy resolution for growing the effectivity and stability of perovskite photo voltaic cells,” they stated.
They introduced the brand new anion defects management technique within the examine “One-stone-for-two-birds technique to attain past 25% perovskite photo voltaic cells,” printed in environmental communication. “Our findings supply an efficient chemical technique for the speedy fabrication of high-performance steady perovskite photo voltaic cells and could also be relevant to different perovskite optoelectronic gadgets,” they concluded.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].