Novel non-contact soldering technique for ribbon tabbing in solar cell manufacturing – pv magazine International

Finnish scientists examined a brand new eddy current-based soldering technique for ribbon tabbing of photo voltaic cells and located that it reduces the variety of cracks and injury brought on by thermal-mechanical stress within the course of. They declare that the brand new method can compete with standard soldering strategies in business manufacturing.
Researchers on the College of Oulu in Finland have developed a non-contact soldering method for ribbon tabbing of PV cells that may scale back thermal and mechanical stress in photo voltaic cell manufacturing, thus avoiding the chance of cracks, disconnected wiring, and hotspots.
Scientists say that assuaging thermo-mechanical stress in solder joints is troublesome, as a result of it happens between two varieties of materials at excessive temperatures within the course of. “The danger of damages brought on by fatigue throughout operation will increase, resulting in excessive collection resistance losses, which creates a terrific problem to optimize the interconnection soldering course of,” they defined.
The newly developed method consists of a brand new soldering technique that should be utilized by a layer of glass. Eddy present, that’s produced by something that causes a change within the depth or path of the magnetic area in a conductor, is a non-destructive technique that may be completed on conductive supplies.
The Finnish group examined this course of on a polycrystalline silicon photo voltaic cell measuring 52 mm x 19 mm x 0.21 mm and having a silver busbar with a width of 1.8 mm in entrance and a 1.8 mm steady soldering pad on the again. Soldering operations are carried out utilizing a microscopic cowl glass slide with a dimension of 76 mm x 26 mm x 1 mm and with solder-coated copper ribbons made from primary lead photo voltaic alloy Sn63Pb37 at a melting temperature from 183 C to 190 C.
“Small weights (34.4 g every) are positioned on the finish of the glass plate to make sure correct contact between the ribbon and the silver busbar,” the lecturers mentioned, noting that the supply used to warmth a Energy Dice 32/900 high-frequency generator supplied by the US-based CEIA, with the heating coil sustaining a distance of round 2.5 mm.
The scientists say that this setting and the induced eddy currents generate native warmth with none direct contact with the heating coil.
Via a collection of checks and microstructural evaluation, they discovered that no further cracks or injury had been detected within the bought cells, apart from some samples. Additionally they confirmed {that a} longer publicity time is best to forestall microcracks inside the solder joint configuration.
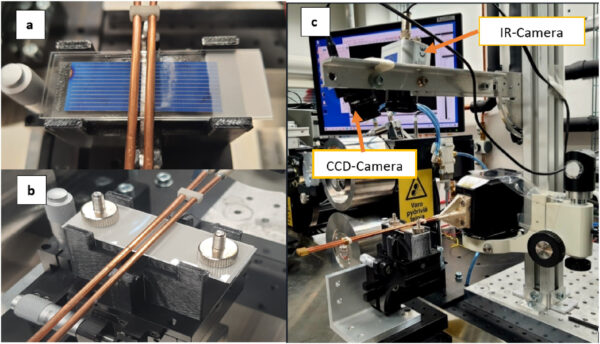
Picture: College of Oulu, Photo voltaic Vitality Supplies and Photo voltaic Cells, Artistic Commons License CC BY 4.0
They concluded that the brand new technique is technically and commercially possible, in addition to aggressive with conventional contact soldering strategies. “Along with ribbon soldering, the proposed method has been developed for use in future research on the restore and upkeep of used photo voltaic panels after failure or elevated collection resistance on account of deterioration because of the passage of time within the tabbing wire or busbar connection with out disassembling the photo voltaic module panel,” additionally they mentioned.
The soldering course of is described within the examine “Eddy present soldering of photo voltaic cell ribbons beneath a layer of glass,” revealed in Photo voltaic Vitality Supplies and Photo voltaic Cells.
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].