Storing renewables via regenerative braking in underground mines – pv magazine International
Austrian scientists have developed a long-term vitality storage system that makes use of regenerative braking to regulate the pace at which sand descends in mine shafts and generate electrical energy.
Researchers led by the Worldwide Institute for Utilized Methods Evaluation (IIASA) in Austria have proposed the usage of regenerative braking to retailer renewable vitality in decommissioned mining websites.
Regenerative braking is an vitality restoration mechanism that extracts wasted vitality from the method of slowing down a car.
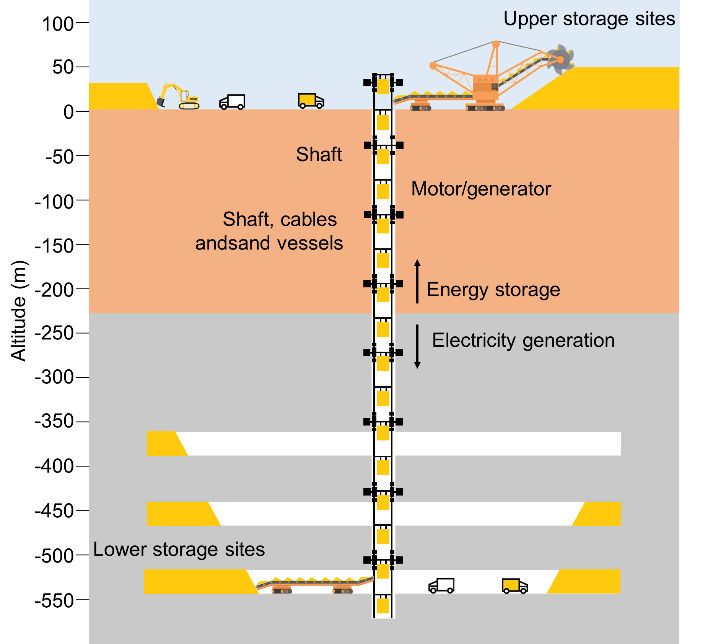
The proposed underground gravity vitality storage (UGES) idea consists of decreasing sand into an underground mine and lifting this sand to an higher reservoir by electrical motors to retailer vitality in periods of low demand. the necessity for electrical energy.
“UGES makes use of regenerative braking to regulate the pace of sand happening the mine shaft and generate electrical energy,” stated researcher Zakeri Benham. pv journal. “It has the benefit of utilizing present infrastructure and offering clear, low-cost, and long-term vitality storage with out materials depth, along with being near the electrical energy grid and roads.”
The system consists of a shaft of various depth and diameter, a motor/generator, higher and decrease storage areas, and mining tools.
“To maximise the ability capability, the sand containers within the shaft occupy roughly 50% of the quantity of the shaft,” the scientists stated. “The opposite 50% of the area is required for filling and emptying containers with sand.”
The charging mode consists of amassing the sand from the decrease storage web site on the backside of the mine with excavators and transporting the sand to the shaft utilizing electrical vans or conveyor belts. Vitality is saved utilizing low-cost or surplus electrical energy from the grid or a big photo voltaic PV farm close by to drag the sand up by way of the shaft utilizing motors/mills. After the sand reaches the highest of the mine, the sand is saved in sand piles.
The discharging mode consists of amassing sand from the higher storage web site above the mine with bucket wheel conveyor belts and transporting it to the mine shaft utilizing a small quantity of electrical energy. Electrical energy is generated by decreasing a heavy quantity of sand down the shaft. Many motors/mills generate electrical energy with regenerative braking alongside the shaft. After the sand reaches the underside of the shaft, it’s transported by conveyor belts or electrical vans to fill your complete caverns of the mine with sand.
“The funding value of UGES is about 1 to 10 USD / kWh and the price of the ability capability is 2.000 USD / kW,” stated the scientists. “The know-how is estimated to have a world potential of seven to 70 TWh, with most of this potential concentrated in China, India, Russia, and the USA.”
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].