Air conditioning based on air cooled photovoltaic-thermal system – pv magazine International
Chinese language scientists have developed a photovoltaic-thermal air con system that makes use of an air-cooled condenser and a PV/T condenser linked in collection. The system reportedly gives higher cooling below night time situations.
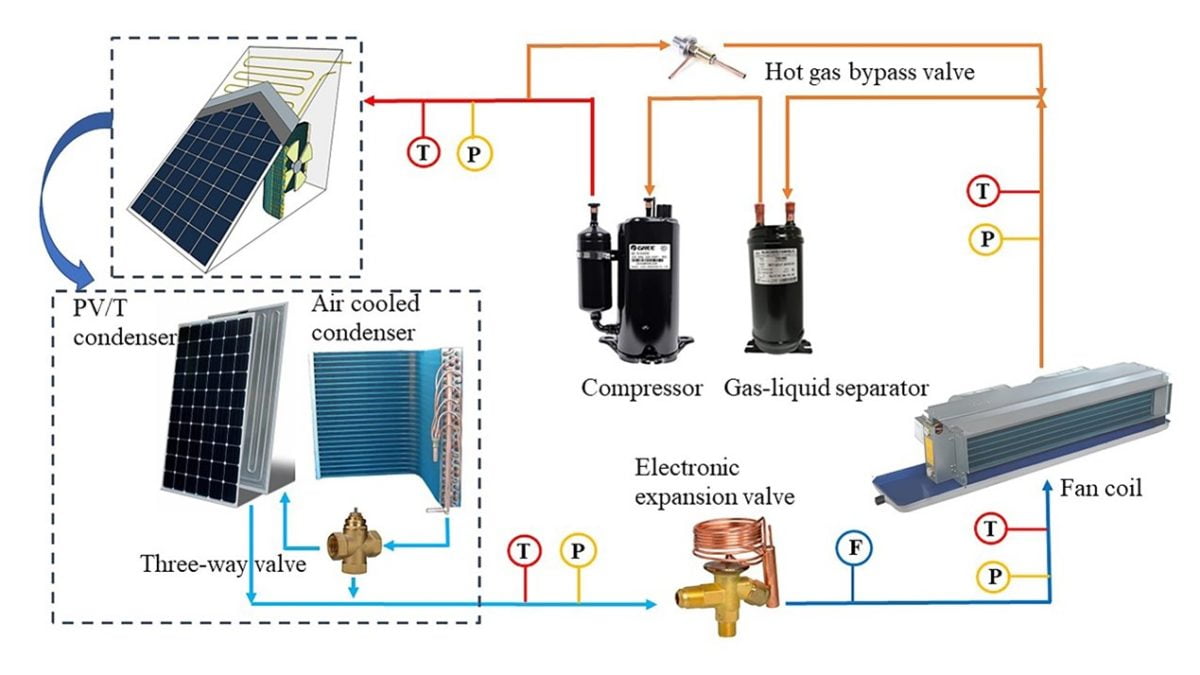
Researchers from Hebei College of Know-how in China has designed a photovoltaic-thermal air con system that makes use of an air-cooled condenser and a PV/T condenser linked in collection.
The innovation of the system consists in using these two parts as an alternative of the generally used ones PV/T warmth exchanger as condenser.
“If photo voltaic vitality and long-wave radiation vitality assets can be found, the proposed system is appropriate no matter the kind of buildings,” stated researcher Man Fan. pv journal. “Qsystem efficiency is improved by complementary use of photo voltaic vitality, windy and excessive–radiation vitality of the wave.”
The PV/T condenser generates energy within the solar and serving to the wind–cooled condenser for warmth loss in the course of the night time. The components of the system an evaporator and condenser, a compressor, the digital growth valve (EEV), a 4–reciprocating valve methodology, a gasoline– liquid separator, and a scorching gasoline bypass valve. It makes use of a refrigerant often known as R410.
“A bypass pipe is put in between the air-cooled condenser and PV/T condenser,” the scientists defined. “By controlling the valves close to the bypass pipe, the system could be modified between an air-cooled PV/T air conditioner and a standard air-cooled air conditioner.”
By opening and shutting three valves, the system can work as the air–cooled PV/T air conditioner or as a typical air–cooled air conditioner.
“The swap between an air-cooled air con system and an air-cooled PV/T air con system primarily will depend on the condensing impact of the PV/T exchanger,” stated the analysis group.
The PV/T condenser consists of a PV plate, an aluminum plate with dimensions of 1580 mm × 810 mm × 2 and 8mm copper tubes from high to backside. the ALUMINUM the plate included behind the PV plate, and copper pipes the welded to the aluminum plate. The air-cooled condenser consists of a fan and fa 8 mm finned tube warmth exchanger. The PV panel used for the system has a width of 1.28 m2, a rated output of 200 W and an influence conversion effectivity of 19.1%.
Lecturers measure system efficiency by utilization Evap-Cond, which is a software program program that provides simulation fashions for finned-tube evaporators and condensers. they discovered that the warmth dissipation fee on condenser system is the “constructive” associated to out of doors air velocity, refrigerant move fee and inlet temperature, and “detrimental” associated to photo voltaic irradiance and outdoors temangle
“When the refrigerant move fee elevated from 10 kg/h to 50 kg/h, the warmth dissipation fee elevated 3.9 instances, and the utmost worth was 3,116.2 W,” they defined “Whereas below different situations , the warmth dissipation fee solely modified by 2.9% to 10.3% with a median worth of three,064.8 W.”
Additionally they discovered that the system cooling capability at night time is about 7.1% and 42.3% longer than a cloudy and sunny day, respectively, and that the system temperature coefficient (COP) is between 2.9 to 4.1which is approx 20.0% and 123.7% larger than a cloudy and sunny day.
“The air-cooled PV/T air con system is recommended to be operated when the photo voltaic irradiance shouldn’t be greater than 200 W,” they stated. “The rise in photo voltaic irradiance and the out of doors temperature are each unfavorable for system cooling and energy cogeneration efficiency.
The researchers launched the system of “The simulation of an air-cooled PV/T air con system for cooling and energy cogeneration,” just lately revealed in Utilized Thermal Power.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].