A analysis group has developed a brand new methodology that reveals that PV techniques situated in the identical space can have the identical distribution of energy ramps. Their three-step methodology can be utilized for measuring roof surfaces and scheduling each day operations.
A gaggle of scientists from DLR Institute of Networked Vitality Methods in Germany proposed using a three-step methodology to quantify the power fluctuations of PV techniques in an effort to estimate the flexibleness potential of buildings and metropolis districts which hosts photo voltaic arrays.
The innovation of the methodology consists in offering not solely the quantity of power that should be reserved or transferred domestically for balancing functions throughout a day, but additionally the required length of the reserve or switch of power.
“The developed methodology distinguishes between energy and power fluctuations in PV techniques,” the lecturers mentioned. “The calculation of energy adjustments requires solely technical traits and time sequence with measured energy values of PV techniques.”
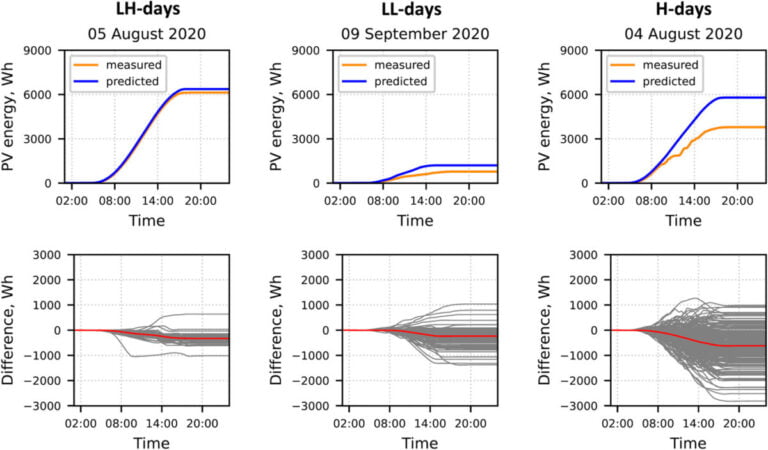
The proposed methodology relies on the evaluation of the so-called energy ramp, which researchers describe because the distinction in energy values between two consecutive cut-off dates in a PV system. The three steps include the classification of days with PV era in “low variability” and “excessive variability,” the calculation of the distribution of PV energy ramps, and the calculation of PV power fluctuations.
This methodology computes the facility ramps at every time level and the power fluctuations per day. “Because the PV energy prediction uncertainties are summed over the entire day, the computed each day power fluctuations might be in contrast with the capability of the native flexibility sources to estimate if the out there flexibility sources have sufficient power to steadiness the each day power fluctuations,” they defined extra.
The analysis workforce examined its methodology on seven PV techniques with capacities from 1.2 kW to 100 kW, situated in northern or southern Germany. By way of this evaluation, it was discovered that days with excessive variability and people with low variability have attribute distributions of PV energy ramps. “The calculated distributions of energy ramps allow the magnitudes of energy fluctuations that always come up in a given PV system to be estimated,” it mentioned. “In different phrases, primarily based on the calculated distributions, the chance of any energy ramp in any PV system might be decided for a given variability class.”
The researchers mentioned the check confirmed that PV installations situated in the identical space ought to have the identical distribution of energy ramps. “Nevertheless, all investigated PV techniques are situated in Germany in western Europe. It might be of educational curiosity to use the developed methodology to PV techniques in different areas with apparently completely different climates and climate situations, they mentioned.
The researchers additionally declare that the brand new methodology can help the enough dimension of PV techniques in buildings and be built-in with power administration techniques for scheduling the operation for the subsequent day.
They describe the brand new methodology within the paper “Calculating energy and power conversion in photovoltaic techniques,” printed in Vitality Science and Engineering. “The proposed methodology for quantifying PV power adjustments might be utilized to any PV system if photo voltaic radiation forecasts for the actual location and technical parameters can be found,” they concluded.
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.