Japanese solar’s struggle for space – pv magazine International

PV Expo and the broader Sensible Vitality Week concluded in Tokyo final week. It revealed bold plans for photo voltaic and power storage installations in Japan, together with inventive methods to take care of the extreme lack of area for brand new installations, which ought to convey extra alternatives for home and worldwide gamers.
Unfold over three days, Japan’s Sensible Vitality Week as soon as once more introduced 1000’s of tourists to the Tokyo Massive Sight. Home corporations are a uncommon sight on the present ground, particularly within the PV Expo corridor. However many individuals and lots of new improvements displayed all through the PV, battery, good grid, and hydrogen exhibitions give lots of hope.
Photo voltaic and renewable power in Japan is usually described as “in a transition interval” in the previous couple of years. Photo voltaic installations stay at a relentless 5 GW to six GW per yr, whereas the discount within the feed-in tariff charge and the dearth of appropriate land for brand new giant PV installations have prompted many to ask what’s subsequent for Japan.
The nation is working in direction of a goal of at the very least 36% to 38% renewables within the power combine by 2030. A gap day presentation by Kazuya Inoue, director of local weather change coverage on the Ministry of Vitality (MoE) of Japan, famous that that is needed. at the very least a doubling of Japan’s cumulative photo voltaic capability, and a big enhance in installations throughout the second half of this decade. Inoue acknowledged that the MoE is “counting on photo voltaic,” and its calculations present that renewable power sources can meet at the very least 1.8 occasions Japan’s complete electrical energy wants – which means way more not exploited. And in response to this, the MoE will create a JPY 20 trillion ($151 billion) fund that shall be used for numerous renewable power, power storage, and decarbonization initiatives till 2030.
With little appropriate land left for large-scale PV, Japan’s PV coverage is shifting focus to rooftop and business PV fashions. Many Japanese corporations have set decarbonization targets for themselves and are in search of to wash up their power provide by way of photo voltaic PPAs. Tokyo-based analysts RTS Corp. defined that prime power costs with subsidies accessible for photo voltaic PPA installations make it a extra engaging mannequin in the intervening time.
RTS additionally mentioned it expects to see the Japanese marketplace for ground-mount photo voltaic installations shrink as residential PV grows. It’s famous that experimental schemes requiring photo voltaic in all new buildings are being examined within the Tokyo and Kawasaki areas, and are prone to be launched within the close to future.
Japan has additionally seen some early installations that mix photo voltaic and agriculture, however opinions are divided on whether or not this agrivoltaics strategy will work as an answer to the dearth of land for photo voltaic initiatives. In response to RTS, agrivoltaics in Japan will possible see some development within the years main as much as 2030, however the Ministry of Agriculture isn’t fairly prepared, and intensive reform of land use laws is required for an actual market to develop.
No extra PERC?
Chinese language cell and module producers dominated a lot of the PV Expo corridor, and wished to showcase their newest merchandise in a market that historically prefers the newest applied sciences. Every of those corporations says plans are effectively underway to cease making PERC cells totally by the top of 2024, and even sooner.
And all of the replacements are on show this week, most taking the only improve route at TOPCon to succeed in larger effectivity. Trina Photo voltaic and JinkoSolar are among the many corporations which have confirmed plans to cease producing PERC altogether. And DAS Photo voltaic, which operates 30 GW of TOPCon cell capability and plans to develop to 40 GW this yr, mentioned pv journal it is “simply getting began for TOPCon,” with expectations to succeed in 26% cell manufacturing effectivity by 2024.
Others, nevertheless, are trying additional into the long run and even larger ranges of efficiency that may be achieved utilizing heterojunction and again contact applied sciences. The producers Huasun and Risen offered their newest heterojunction merchandise, with the primary focusing on a median effectivity of manufacturing cells of higher than 25% and planning to develop its capability to 40 GW in 2025.
Longi Photo voltaic additionally has its newest hybrid passive again contact merchandise on the present, and Aiko Photo voltaic is exhibiting its newest All-Again-Contact, which is its rolling out merchandise for the rooftop. market this yr and is predicted to scale back prices sufficient for giant. -scale characteristic within the subsequent few years, in addition to attaining higher than 27% module effectivity.
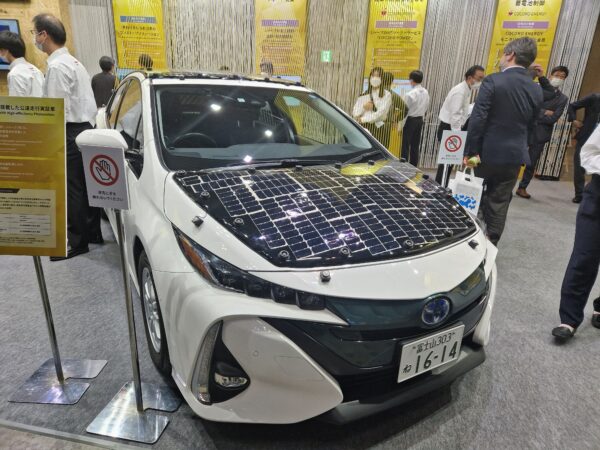
Electronics big Sharp – which appears to be the one Japanese firm to indicate any kind of PV module at this yr’s present – is exhibiting off its multi-junction gallium-arsenide primarily based cell, which hits greater than 30% effectivity. At the moment at greater than 100 occasions the price of a typical silicon cell, there’s a lengthy method to go earlier than it turns into engaging for powering something aside from area journey. Nonetheless, the corporate has proven a Toyota automobile coated in these cells, including as much as a powerful 860 W of solar energy to the automobile’s physique, which the corporate says can run a single journey. as much as 50 km with out one other cost.
Sharp additionally mentioned it’s working with the New Vitality and Industrial Know-how Improvement Group (NEDO) to convey the price of these cells right down to earth. They’ve developed a reusable substrate and bigger processes to chop greater than a 3rd of the overall value, however do not anticipate to see it on a rooftop anytime quickly.

Picture: pv journal/Mark Hutchins
Japan, like many different markets with a rising share of renewable power, realizes that it must do main work on its electrical energy networks to offer everybody with clear power when and the place. it should. And the Sensible-Grid expo is a spot the place well-known Japanese manufacturers can shine much more. Mitsubishi Electrical has completely different software program on show, which reveals that it might probably handle giant energy networks by combining knowledge from many small installations right into a digital energy plant.
Sharp, in addition to Chinese language corporations Growatt and Sungrow, additionally demonstrated electrical automobile chargers and previewed vehicle-to-grid and vehicle-to-home approaches, the place the automobile’s battery whereas plugged in is used to maximise the consumption of photo voltaic electrical energy from the roof set up. , or many are linked to develop it throughout the area. It is an strategy that corporations anticipate to realize extra traction in Japan within the coming years, particularly within the residential section.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].