Micro-hydroelectric power generator for sewage treatment plants – pv magazine International
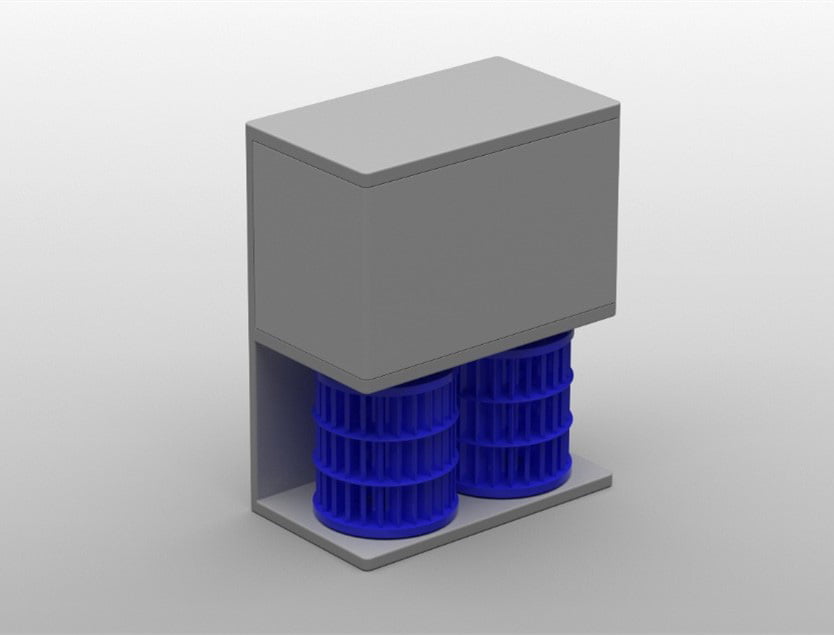
Japan’s Ricoh has designed a micro hydropower system for sewage crops that would doubtlessly be utilized in mixture with ground-mounted photo voltaic or floating PV. The system encompasses a sustainable water turbine designed by micro-hydroelectricity specialist Seabell Integrated and the Kanazawa Institute of Know-how.
Ricoh of Japan has developed a micro hydropower system that can be utilized in sewage remedy facility, with sewage water serving as a supply for low-head screw generators.
The imaging and electronics firm mentioned the electrical energy generated by the micro-hydro system can be utilized to energy sewage crops.
“Right now, now we have not carried out any checks concerning the mixture of our PV system or floating PV,” mentioned an organization spokesperson. pv journal. “Nonetheless, we imagine there may be potential for PV to be built-in into our system sooner or later, as a result of great amount of house accessible at sewage websites.”
The system encompasses a water turbine designed by the corporate in collaboration with micro-hydroelectric system provider Seabell Integrated and the Kanazawa Institute of Know-how. It consists of two turbines put in in a single unit, which permits environment friendly technology of electrical energy. As well as, a water wheel might be positioned straight within the current water channel, eliminating the necessity for a brand new water channel bypass. Ricoh supplied the 3D printing know-how to create the 3D printed blades used within the system. It’s made from supplies obtained from biomass.
“In comparison with a water turbine made out of generally used 3D printer supplies, our turbine is greater than twice as highly effective as a metallic turbine,” the spokesperson mentioned. “Its vitality is maintained even when positioned underneath water for a very long time and can be utilized for large-scale hydroelectric energy technology.”
Ricoh carried out the primary demonstration experiments at a sewage remedy plant in Shizuoka prefecture, Japan, in collaboration with the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) of Japan. The venture is designed to handle a number of points concerning using micro-hydroelectric methods in sewage services. These points embody low turbine effectivity, low output, excessive upfront prices, and the intensive use of human assets. The electrical energy generated by the micro-hydro system can be utilized for backup energy provides in disaster-prevention facilities and sewage remedy crops.
“The system will initially be offered in Japan however we proceed to discover the potential of introducing our know-how to different areas, together with Europe, america, and rising economies,” mentioned the spokesperson.
In March, Ricoh launched a pico-hydro technology system that can be utilized in manufacturing unit drainage methods and irrigation canals.
“The system can be utilized in mixture with photovoltaics and batteries to make sure a secure energy provide,” an organization spokesperson mentioned. pv journal. “Relying on the quantity of electrical energy generated, it may be used for IoT units reminiscent of sensors, lighting units, and charging methods.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].