New method to avoid overvoltage in vertical PV linked to low-voltage grids – pv magazine International
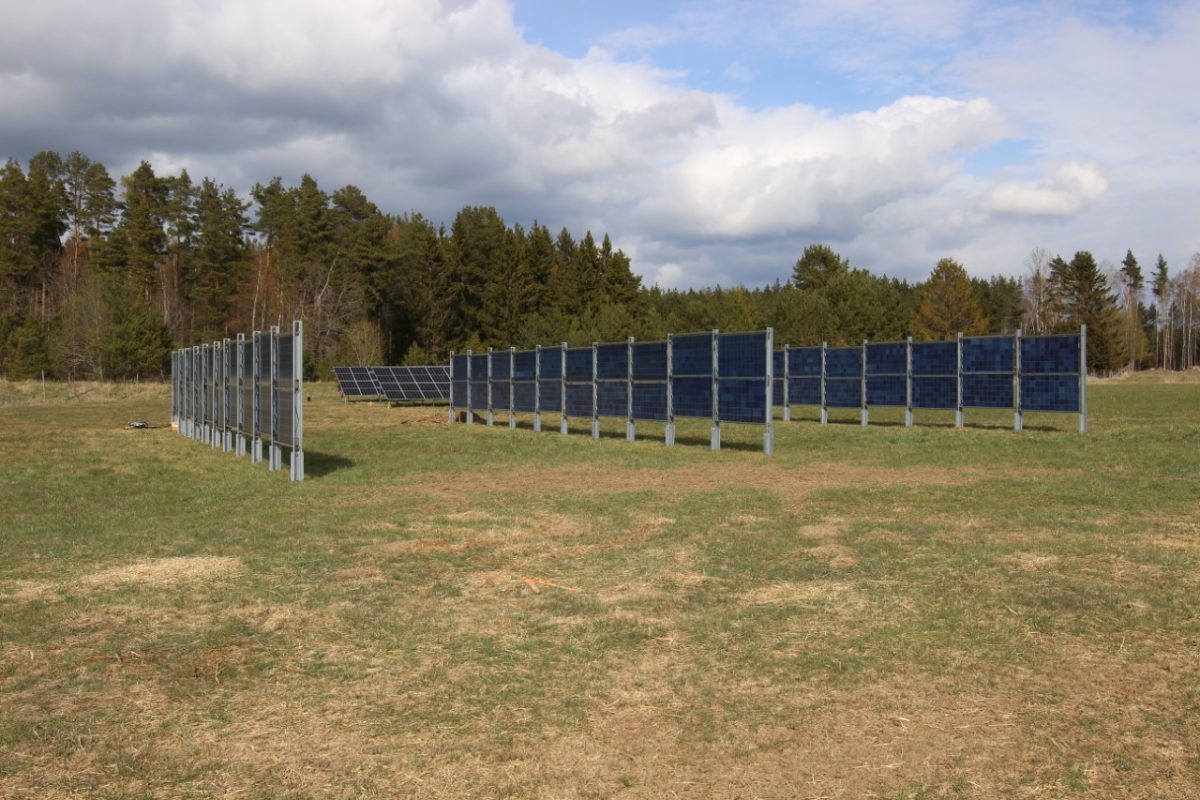

A Finnish analysis group has developed a brand new workflow to forestall voltage surges in bifacial vertical PV methods situated at excessive latitudes. In accordance with their findings, vertical bifacial PV can have a 46% greater energy yield in comparison with monofacial typical counterparts within the Nordics, whereas there’s additionally an improved temporal match between PV technology and consumption.
Researchers on the College of Turku in Finland have developed a methodological workflow to enhance the facility yield of bifacial vertical PV methods linked to low-voltage (LV) grids situated at excessive latitudes and with completely different panel places, orientation, and expertise.
They defined that their new technique is meant to keep away from the rise in community voltage, which happens when PV technology exceeds demand, with excessive voltages that may harm the grid itself and {the electrical} units linked to it. this. “Subsequently, the voltage should be restricted beneath a threshold by figuring out the utmost allowed PV capability within the distribution grid or by setting a restrict on the utmost allowed PV manufacturing and stopping extra manufacturing ,” they defined.
The brand new technique works by means of 5 predominant steps: information assortment, decomposition modeling, transposition modeling, electrical and thermal modeling, and LV grid evaluation. The second and third steps present a calculated international tilted irradiance (GTI) profile for the chosen location, time, and PV orientation, which is then transformed to PV energy output, taking into consideration the info of climate and PV system properties. The evaluation of the LV grid prevents oversizing the PV system to keep away from overvoltage.
The scientists utilized the workflow to completely different circumstances of monofacial initiatives and bifacial vertical PV methods. They analyzed the PV manufacturing profile, energy load profile, and the mix of PV internet hosting capability variables, which they are saying are essential components in avoiding overvoltage occasions.
By way of their evaluation, the teachers ascertained that the utmost allowed PV capability is often restricted to brief temporal durations with a length between 1 and half-hour. These phases are characterised by excessive PV technology and sudden modifications in electrical load and PV manufacturing. “It emphasizes that managing such durations with completely different voltage regulation units or permitting over- and undervoltage occasions to happen within the brief time period can improve the PV internet hosting capability, ” they mentioned.
In accordance with their findings, vertical bifacial PV can have a 46% greater energy yield in comparison with monofacial typical counterparts within the Nordics, whereas there’s additionally an improved temporal match between PV technology and consumption.
The brand new technique is introduced within the paper “A complete methodological workflow to maximise photo voltaic vitality in low voltage grids: A case examine of vertical bifacial panels in Nordic situations,” revealed in Photo voltaic Vitality.
“Additional work is required to incorporate extra reasonable electrical energy load fashions and financial evaluation of the method,” the Finnish group concluded. “Moreover, because the used take a look at community covers solely a really small geographic space, leading to low losses of energy strains, it’s prone to overestimate absolutely the values of the utmost PV manufacturing in comparison with most distribution grids in the true world, though it permits the comparability of the relative values between completely different circumstances.”
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].