Chinese language scientists have developed a brand new swelling course of to take away glasses and EVA backsheets from photo voltaic modules on the finish of their life cycle. The approach makes use of an ester of a dicarboxylic acid often called a dibasic ester. It reportedly prevents extreme cracking of photo voltaic cells.
A analysis crew from the Chinese language Academy of Sciences, and China-based photo voltaic panel maker JinkoSolar, have developed a brand new swelling course of to separate the glass and backsheet based mostly on ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) from photo voltaic cells in end-of-life modules.
“Our irritation course of shouldn’t be violent and managed,” stated Wang Dong, the lead creator of the analysis. “It doesn’t destroy photo voltaic cells and ensures a excessive effectivity recycling fee of cells and valuable metals. As well as, it has little or no toxicity and the swelling agent will be recycled.
Within the paper “Recycling of photo voltaic cells from photovoltaic modules by way of an environmentally pleasant and controllable swelling course of utilizing dibasic ester,” revealed in Clear Know-how and Environmental Insurance policiesscientists defined that the method makes use of a dibasic ester (DEB), which is an ester of a dicarboxylic acid that’s typically used as a lubricant, spin end, and additive.
“DBE is a promising inexperienced solvent broadly used within the coating business which is an ester combination consisting of dimethyl succinatedimethyl glutarate, and dimethyl adipate,” they stated. “Moreover, DBE has a boiling vary of 196 C to 225 C and may soften most resins.”
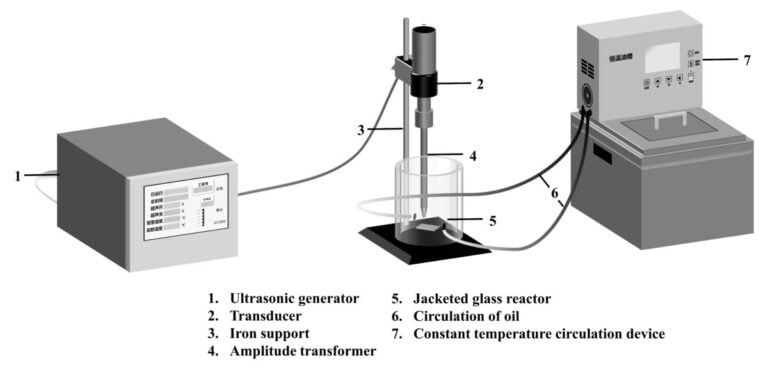
the DBE admits enters the glass-EVA hole successfully whereas preventing the moisture within the air from getting into the separation system hydrolyze DBE. Within the subsequent step, an ultrasonic discipline is used promote separation of glass-EVA.
“Then the separation system will be filtered to get a glass and (photo voltaic cell + EVA) composition. Lastly, the combination is sieved to acquire (photo voltaic cell + EVA), and the EVA will be eradicated by pyrolysis to be sufficiently recovered the photo voltaic cells,” the researchers continued. “In distinction to the direct thermal course of, no fluoride is launched throughout EVA pyrolysis because of the preliminary removing of the backsheet.”
The crew examined the novel approach on a Jinko 535 W photo voltaic module measurement 1,956 mm x 992 mm and weight 22.5 kg, with the junction field and aluminum body eliminated advance. It performs the separation of glass-EVA in a glass reactor with a backside diameter of 120 mm × 12.5 mm and a top of 195 mm × 20 mm.
By these measurements, scientists discovered that the decrease swelling of DBE resulted in fewer cracks in comparison with a swelling course of based mostly on the generally used O-dichlorobenzene. In addition they famous that the value of O-dichlorobenzene is between CNY 16,000 ($2.316) and CNY 18,000 per ton, whereas the price of DBE beneath between CNY 9,500 and CNY 10,600 per ton.
“In conclusion, use DBE to separate the glass-EVA can maintain the relative integrity of EVA to make useful resource restoration extra manageable, and utilizing DBE as a separation reagent has some great benefits of low price and inexperienced environmental safety,” emphasised Dong. “Detailed price accounting, nevertheless, will probably be accomplished this 12 months after the scale-up check.”
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.