New York City’s Vehicle Emissions Get Absorbed by Its Greenery on Many Summer Days, Study Finds
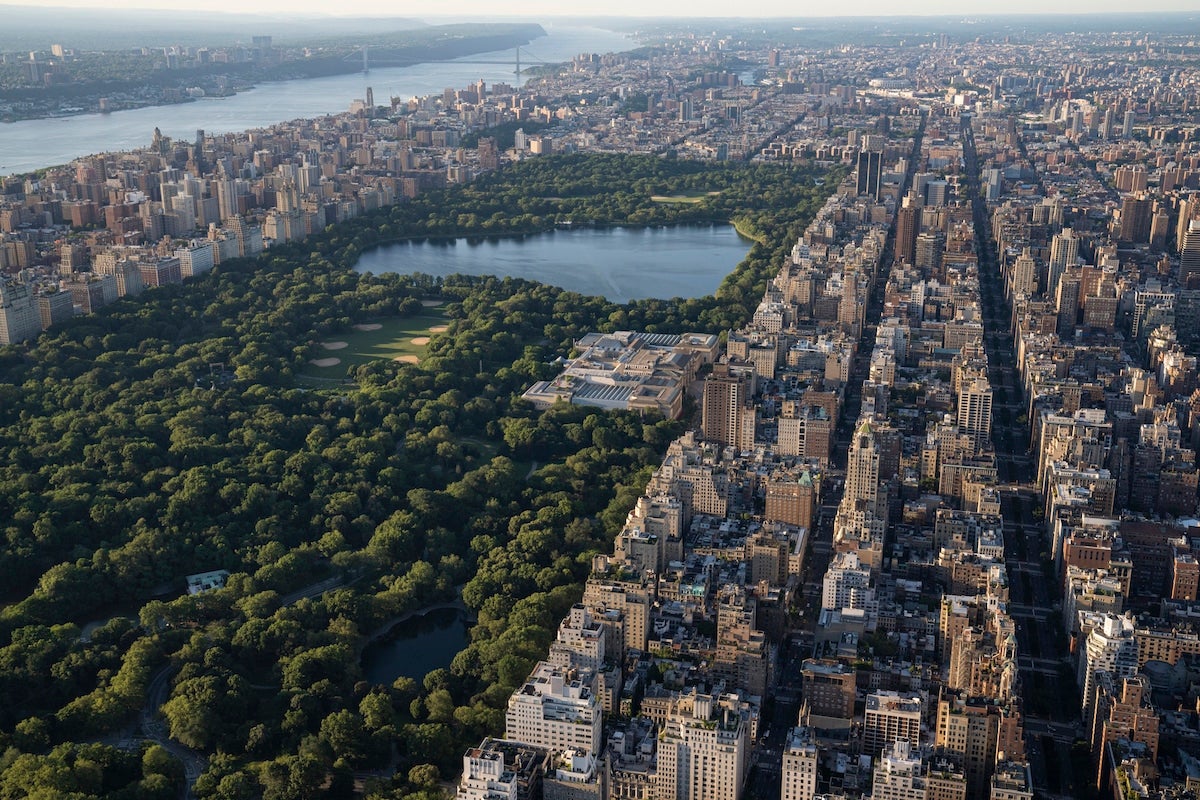

An aerial view of New York Metropolis. Nisian Hughes/DigitalVision/Getty Photos
Why you may belief us
Based in 2005 as an Ohio-based environmental newspaper, EcoWatch is a digital platform devoted to publishing high quality, science-based content material on environmental points, causes, and options.
A current research of New York Metropolis’s vegetation discovered that a rare quantity of the town’s vehicular carbon emissions – along with some neighboring areas – are absorbed by grasses and bushes. On many summer time days not solely all carbon dioxide emissions from buses, vehicles and vans are absorbed by the greenery of the world, however some further emissions as properly.
The research used high-resolution native vegetation maps to report small patches of inexperienced that have been beforehand ignored, some in extremely developed areas, mentioned a press launch from the Columbia Local weather College. Researchers have discovered that the method of photosynthesis in greens contributes tremendously to the change of carbon dioxide emissions for sugars and oxygen.
“There’s extra inexperienced than we thought, and that drives our conclusion,” mentioned postdoctoral researcher at Columbia Local weather College’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Dandan Wei, who was lead creator of the research, reported Yale E360. “It tells us that the New York Metropolis ecosystem is necessary, and if it is necessary right here, it may be necessary in all places.”
City areas produce greater than 70 p.c of the carbon dioxide emitted by people, with New York Metropolis being the third largest emitter of greenhouse gases on this planet and the most important within the US, the press launch mentioned.
The research, “Excessive-resolution modeling of vegetation reveals massive biogenic CO2 fluxes in summer time in New York Metropolis,” is revealed within the journal Environmental Analysis Letters.
In earlier research, scientists have principally examined contiguous areas of grassland and forest, which solely make up about 10 p.c of the town.
The brand new aerial radar photos utilized by the researchers mapped the town’s vegetation on six-inch grids that included areas that weren’t in earlier representations, equivalent to vacant tons, a tree streets, backyards and different small areas. About one-third of the 837.8 sq. miles complete research space spans the 5 boroughs of New York Metropolis and is split into roughly 98-foot grids.
“Most individuals imagine that New York Metropolis is only a grey field, that it’s biogenically useless,” mentioned Lamont-Doherty atmospheric chemist Roísín Commane, a co-author of the paper, within the press launch. “However simply because there is a concrete sidewalk someplace doesn’t suggest there is not additionally a tree shading it.”
The researchers discovered that 22 p.c of New York Metropolis – or 65.64 sq. miles – is roofed in bushes, and about 12 p.c – or 36.29 sq. miles – is roofed in grass.
To learn how all this greenery impacts the town’s carbon dioxide emissions, researchers checked out knowledge from June to August of 2018, when the New York metro space produced about 14.7 million tons of carbon.
The research discovered that the most important emitters of carbon dioxide are vehicles and the vitality utilized in buildings. Commane mentioned the typical degree of carbon dioxide in New York Metropolis is persistently 460 elements per million or extra, whereas the worldwide common is about 417.
In response to the research, these ranges can be better if it weren’t for the greenery. In developed elements of the town it’s accountable for virtually 85 p.c of every day carbon absorption.
The research discovered that through the excessive variety of summer time days, 40 p.c of carbon emissions from all sources are absorbed. Carbon ranges have been discovered to extend within the morning and reduce considerably within the afternoon. Wei mentioned in cities with climates hotter than New York, crops are inclined to have a better affect.
The analysis crew has plans to broaden their research of city bushes to species sorts to disclose their particular advantages. Oaks are frequent within the area, however are decided to supply a compound – isoprene – that reacts with automotive emissions to supply ozone, an air pollutant.
“Extra bushes can at all times be higher, it doesn’t matter what they’re,” Wei mentioned within the press launch. “However we might use an evaluation of who’s the most effective.”
Subscribe to get unique updates in our every day publication!
By signing up, you comply with the Phrases of Use and Privateness Coverage & to obtain digital communications from EcoWatch Media Group, which can embrace advertising promotions, commercials and sponsored content material.





