Novel attempt to design solar cells based on zinc phosphide – pv magazine International
European researchers checked out how zinc phosphide might be utilized in photo voltaic cell improvement and located that monocrystalline skinny movies can carry out higher than polycrystalline movies in electrical units. . Additionally they decided that the efficiency of such movies is straight associated to the zinc/phosphide ratio.
A world analysis workforce led by Switzerland’s Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) appeared on the electrical properties of zinc phosphide (fZn).3Q2), in one other try to contemplate its use as an absorber materials in photo voltaic cells. Presently, cells primarily based on fZn3Q2 attain a really restricted energy conversion effectivity, because of the intrinsic limitations of their electrical properties, comparable to minority service mobility and service diffusion lengths.
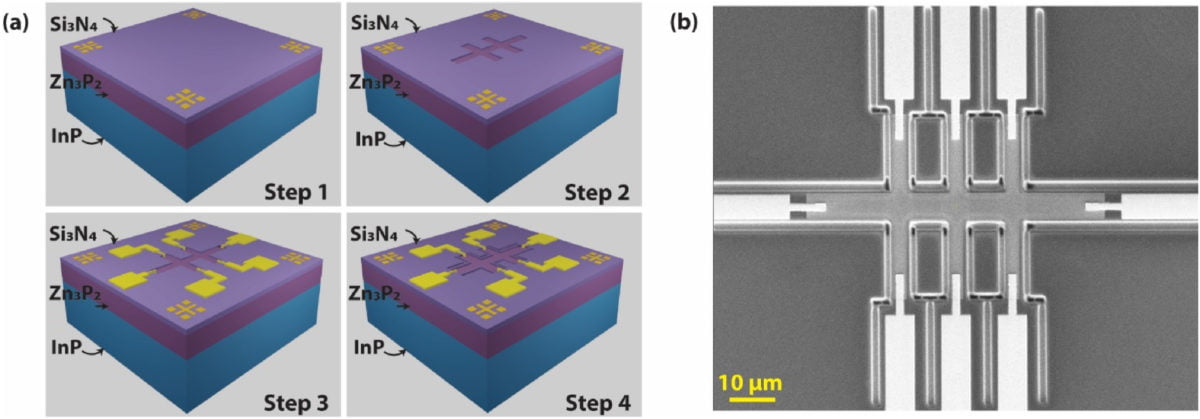
The scientists describe their findings in “The Zn/P ratio and microstructure outline the service density and electrical transport mechanism of soil-abundant Zn3-xQ2+y skinny movies,” which was not too long ago revealed in Photo voltaic Power Supplies and Photo voltaic Cells. They investigated {the electrical} properties, in addition to the chemical composition and microstructure, of polycrystalline and monocrystalline Zn3Q2 skinny movies grown on indium phosphide (InP) substrates.
“We’ve demonstrated a tool fabrication approach that avoids the challenges arising from micro-cracks current in monocrystalline skinny movies,” they stated. “Temperature-dependent measurements elucidate defect states and their contribution to Zn transport3Q2 skinny movies. We thus exhibit that the expansion situations play an vital position in figuring out {the electrical} properties of given skinny movies.
The group has developed a number of electrical units primarily based on skinny movies grown on each doped (each n- and p-type) and undoped InP substrates. They in contrast their efficiency with respect to the current-voltage attribute of Zn3Q2/InP heterojunction. They deposited Zn3Q2 movies by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD).
Teachers discovered that poly-Zn3Q2 skinny movie has a tough floor, whereas the mono-Zn3Q2 skinny movie has a easy cross-sectional morphology and comparatively flat floor. Additionally they decided that mono-Zn3Q2 skinny movie has a resistivity worth within the vary of 150 Ω cm to 1,050 Ω cm and the previous within the vary of 6,500 Ω cm to 9,000 Ω cm.
“The massive distinction in resistivity worth may be attributed to the presence of grain boundaries in poly-Zn.3Q2 skinny movies, which contribute to the elevated dispersion of cost carriers,” the scientists defined.
Additional evaluation reveals that mono-Zn3Q2 The movie can obtain a lot larger present density values in comparison with poly-Zn3Q2 tools. The researchers attributed the low worth of the present density of the polycrystalline skinny movie to the excessive resistivity of the fabric.
“Top quality monocrystalline Zn3Q2 Skinny movies with average service focus exhibit excessive gap mobility (125 cm2/ Vs) at room temperature, which signifies the expansion situations and composition of the fabric play an vital position in tuning the performance of the fabric,” the researchers stated. “We reveal the impact of unintentional doping that causes adjustments within the Zn/P ratio on {the electrical} properties of the fabric.”
Their conclusion is that the focus of the service within the instruments is straight associated to the Zn/P ratio.
“This work sheds mild on {the electrical} properties and conduction mechanism, thus offering a greater understanding of the constraints and potential {of electrical} units associated to the fabric,” stated the researchers.
The group consists of scientists from the Universidad de Salamanca in Spain.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].