Novel oxygen-ion battery may offer longer lifespan, claims TU Wien – pv magazine International
Austrian scientists have developed a lab-scale, solid-state, oxygen ion battery based mostly on blended ionic digital conducting (MIEC), which is a particular kind of non-combustible electroceramic supplies. The battery has about 30% of the vitality density of lithium-ion batteries however can supposedly obtain an extended life.
Researchers from the Vienna College of Know-how (TU Wien) have developed an oxygen-ion battery that’s mentioned to rival lithium-ion batteries with “extraordinarily lengthy life,” based on a TU Wien assertion.
Scientists have proven that blended ionic digital conducting (MIEC) perovskite-type oxides, electroceramic supplies generally utilized in strong oxide gas and electrolysis cells, can be utilized to create a solid-state oxygen ion battery that operates at 350 C as much as 500 C.
“These oxygen ion batteries could supply some benefits over different battery applied sciences, corresponding to [lithium-ion], sodium sulfur, or ZEBRA batteries,” the lecturers mentioned. “Consisting solely of strong, non-flammable oxides, they current little or no safety threat in case of system failure. As well as, they are often made in bulk from many parts, and particularly, don’t rely of crucial parts corresponding to cobalt or lithium.
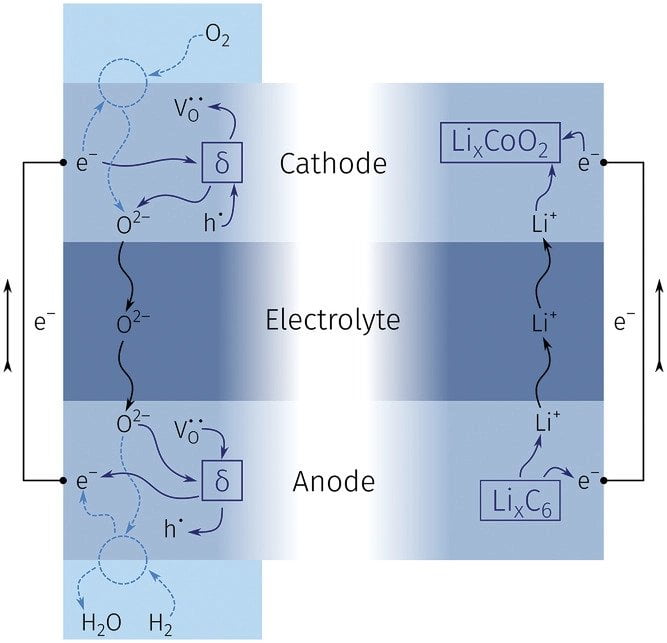
The staff used a ceramic materials known as yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) with MIEC skinny movie electrodes as mannequin cells. These ceramic supplies can take up and launch double destructive oxygen ions. When an electrical voltage is utilized, the oxygen ions transfer from one ceramic materials to a different, after which they will migrate again once more, thus producing an electrical present.
“That is similar to lithium-ion battery electrodes, which retailer electrical vitality by altering the lithium content material. Basically, voltage-driven modifications in oxygen stoichiometry correspond to charging / chemical capability discharge, the place self-discharge via the trade of atmospheric oxygen is prevented,” the researchers defined.
Crucially, they consider that exchanging oxygen with the environment within the different course can result in an extended battery life.
“The oxygen-ion battery may be regenerated with out issues: If oxygen is misplaced on account of aspect reactions, then the loss may be compensated by oxygen from the ambient air,” says TU Wien.
Teachers create full-cell solid-state oxide batteries by combining two electrodes with completely different oxygen entry potentials and use them to foretell the efficiency of an optimized solid-state oxide ion battery.
The outcomes present volumetric vitality densities of as much as 140 mW h cm-3, which corresponds to nearly 30% of the volumetric vitality density of present lithium-ion batteries, based on scientists. DC measurements of the cell present capacities as excessive as 120 mA h cm-3 in a cell voltage of 0.6 V at 350 C to 400 C. Each of the electrodes present biking efficiency with faraday efficiencies above 99%.
“When you want a big vitality storage unit to briefly retailer photo voltaic or wind vitality, for instance, the oxygen-ion battery may be a superb resolution,” says researcher Alexander Schmid . “When you construct an entire constructing stuffed with vitality storage modules, the low vitality density and the elevated working temperature don’t play a big function. However the strengths of our battery are a lot essential there: the lengthy service life, the opportunity of making many supplies with out uncommon parts, and the truth that there isn’t a threat of fireside in these batteries.
The authors share their findings in “Rechargeable Oxide Ion Batteries Based mostly on Combined Conducting Oxide Electrodes,” not too long ago revealed in Superior Vitality Supplies. They submitted a patent software for his or her invention.
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].