Whereas this initially had a chilling impact on the Polish residential photo voltaic market, the transition from web metering to web billing additionally resulted in optimistic modifications, comparable to higher sizing of rooftop PV methods and better charges of self-consumption, says Instytut Energetyki Odnawialnej (IEO), a Polish analysis physique.
Early April will mark a yr because the photo voltaic sector in Poland underwent a profound change, when new provisions had been launched for PV “micro-installations” as much as 50 kW in dimension . The brand new web billing system replaces the web metering scheme, which has been the principle PV deployment engine within the nation since its introduction in 2016.
In response to IEO, the primary results on prosumers could be seen in final yr’s set up numbers, however the affect of the change on buyers and installers is just not but clear. About 1.3 GW of micro-installation PV capability shall be linked within the first quarter of 2022. About 152,000 methods have been put in with a mean energy of 8.3 kW. This equates to roughly 1,700 installations per day. After the transition to web billing, this quantity dropped to 375 MW within the third quarter.
“The web billing system is slowing down the expansion of prosumer installations, however not as a result of it’s a unhealthy resolution,” the IEO stated. “It is about accepting and studying new guidelines by installers and prosumers, in addition to understanding them by banks and monetary establishments.”
It additionally factors to the optimistic results of the web charging regime, together with higher metering of PV installations and investments in extra tools to make use of extra photo voltaic vitality, comparable to warmth pumps and methods to retailer battery vitality.
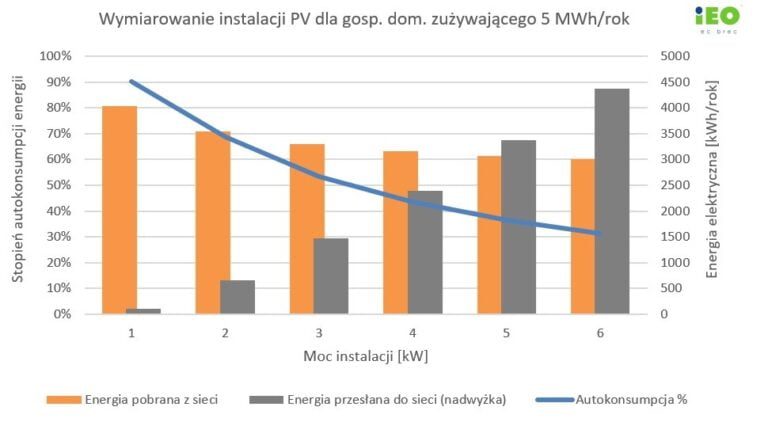
In response to the IEO, the brand new system of net-billing results in the next fee of self-consumption. It says that beneath the web billing system, with the help of the Mój prąd (My Electrical energy) rebate program, prosumers with investments in small PV installations of 4 kW to five kW will get a greater inside fee of return (IRR) of 19% to 25%. The web-metering regime gives an IRR of 13% to 14%.
Underneath the previous net-metering guidelines, house owners of PV methods with a capability of lower than 10 kW may inject as much as 80% of their energy into the grid, whereas PV methods from 10 kW to 50 kW are allowed to feed as much as 70% of their electrical energy to the grid. Underneath the brand new net-billing guidelines, prosumers should put together a invoice that features the vitality they generate. The worth is then calculated based on a particular mannequin associated to the worth of a kilowatt-hour through the so-called “each day buying and selling.”
Prosumers account for nearly 80% of the put in PV capability in Poland. On the finish of final yr, the variety of prosumers exceeded 1.2 million, and the overall capability of their installations amounted to greater than 9.3 GW. Which means that the common energy of a micro-installation is 7.6 kW.
The IEO energy forecast assumes that the nation’s cumulative PV capability will stand at 20 GW in 2025. In 2030, this determine ought to attain 29 GW, together with 15 GW of prosumer energy sources, together with 4 GW of PV methods owned by companies.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.