PV-powered offgrid air conditioner for building applications – pv magazine International
A British analysis group investigated the technical feasibility of an air-con unit powered completely by solar-plus-storage and located that two 130 Ah batteries charged by two 400 W photo voltaic panel has the flexibility to help the system at evening.
Researchers from Ulster College in the UK have developed a mini-split air-con mattress unit powered solely by off-grid solar energy and battery storage.
“This technique has nice potential to serve low-income households in growing international locations, because it requires a lot much less enter energy,” they mentioned within the paper.A Photo voltaic Powered Off-Grid Air Conditioning System with Pure Refrigerant for Residential Buildings: A Theoretical and Experimental Analysis,” printed in Cleaner Power System. “This technique affords a extra energy-efficient various to traditional break up models by cooling a cover at evening.”
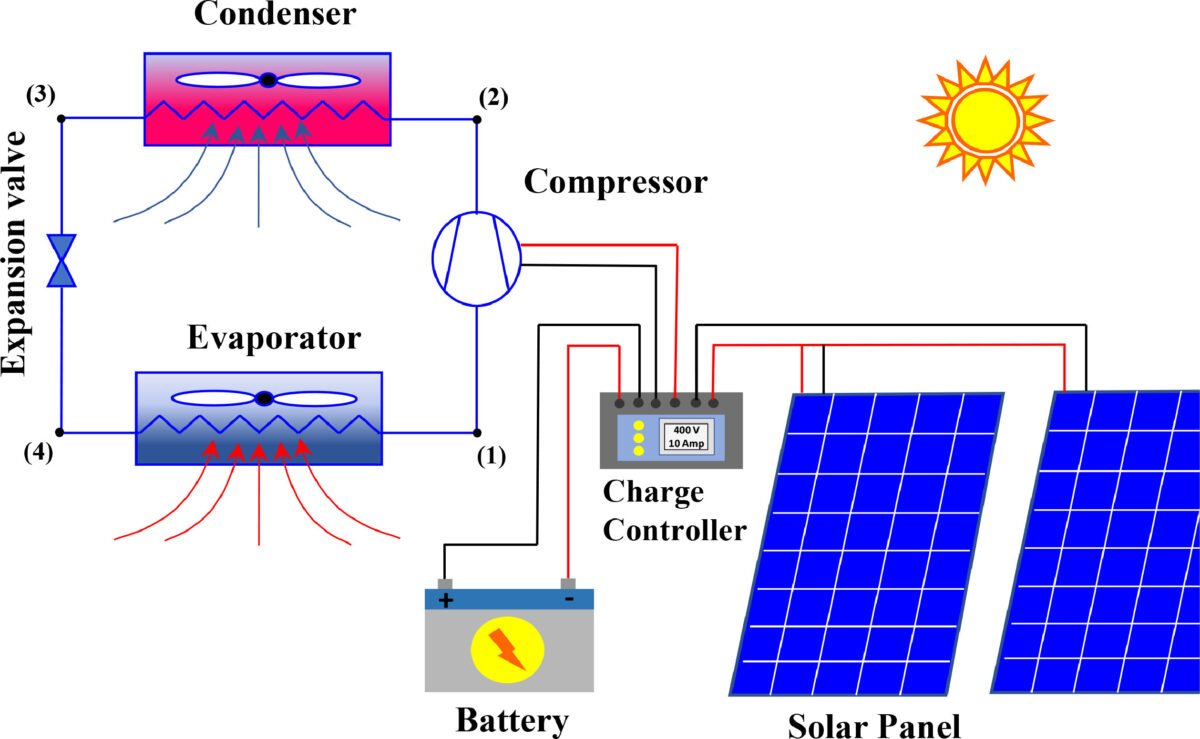
The system, which scientists say is designed to work low international warming potential (GWP) refrigerants, consists of two 400 W photo voltaic panels, two 130 Ah lead-acid batteries, and a vapor compression cycle (VCC) unit.
The exterior unit consists of a compressor, a condenser, an growth valve, and two batteries related in parallel to a cost controller and inverter. The inner unit consists of an evaporator, exterior ducts, and an indoor unit. “The inner elements encompass the cover, provide and extract flex ducts and the AC unit,” defined the analysis group.
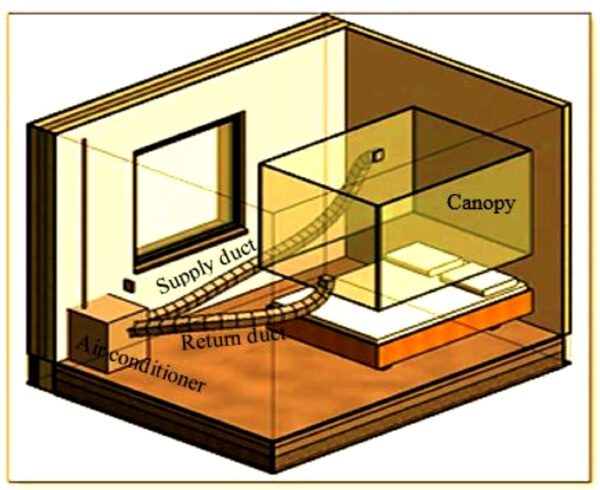
Picture: Ulster College, Clear Power Methods, Artistic Commons License CC BY 4.0
The proposed system configuration is believed to be working in Abu Dhabi, UAE. The scientists mentioned that the simulation was accomplished at completely different condensation temperatures and confirmed that the batteries charged by the photo voltaic panels are in a position to help the air-con unit in the course of the evening.
The system is assumed to run throughout summer season, with an working temperature of 35 C to 40 C and an working humidity of between 50% to 60%.
Scientists have recognized the GWP refrigerants R600a and R290 as the perfect candidates to switch the generally used R134a and R410A. “In comparison with R134a, the experimental coefficient of efficiency (COP) of R290 elevated by 2.42%, with a decrease enter work of two.31% and a higher exergetic effectivity of two.37%,” they defined, noting that the COP confirmed on the highest worth for all candidates because the temperature enhance decreases. “Lowering the temperature rise between the evaporator and condenser improves system efficiency.”
Additionally they discovered that the unit utilizing the R290 required lower than a 3rd of the horsepower and that the 2 batteries had been sufficiently charged to function the system for seven hours. “These outcomes present that the unit is virtually possible,” they concluded.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].