What Is a Hydrogen Energy Storage System and How Does It Work?
Modern society faces a key challenge regarding effective clean energy storage amid its changeover from traditional power sources. Hydrogen energy storage systems have emerged as a capable storage technology people view as the future solution to deliver sustainable power at critical times.
A hydrogen energy storage system represents what forms the basis of this system construction together with its operational protocol. I will present the explanation in basic language.
What Is a Hydrogen Energy Storage System?
The hydrogen energy storage system uses renewable energy excess from solar or wind resources to transform it into hydrogen gas. The stored hydrogen functions as both an electric power generator and an alternative fuel source.
Using this method provides you with a convenient way to conserve extra electricity which can be stored as hydrogen for future use. Solar panels together with wind turbines generate electricity beyond demand which stays safely stored as hydrogen gas through their system. The excess energy becomes hydrogen for later usage particularly when energy production decreases.
How Does It Work?
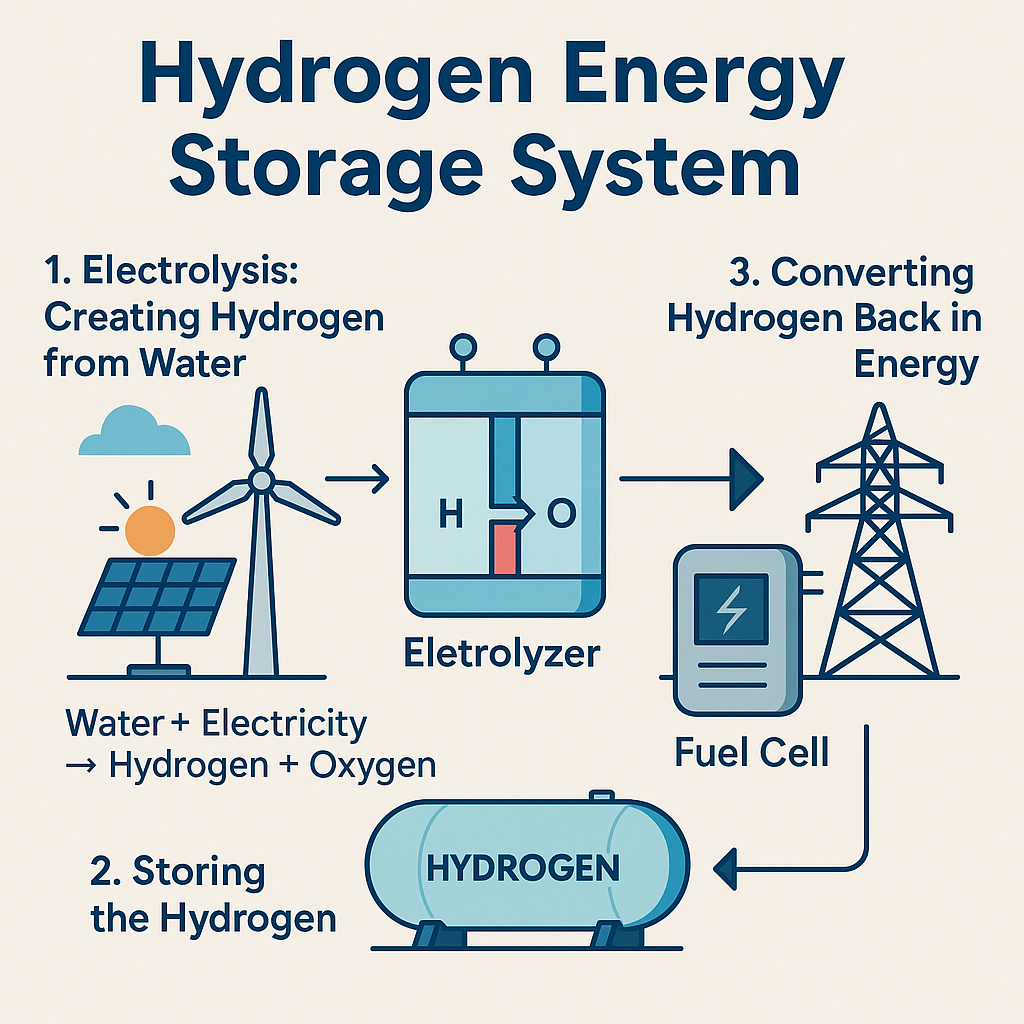
Hydrogen energy storage operates in three main steps:
1. Electrolysis: Creating Hydrogen from Water
The first step brings water to electrolysis to create hydrogen gas and oxygen gas by running power through it. Renewable power generation of electricity leads to the production of green hydrogen.
The electrolytic device named electrolyzer performs this splitting process. The electrolysis system divides water (H₂O) into its basic substances of hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂).
In short: Water + Electricity → Hydrogen + Oxygen
2. Storing the Hydrogen
Storing the Hydrogen The generated hydrogen finds storage in tanks which use pressure levels or low temperature conditions alongside metal hydrides materials. Hydrogen demonstrates superior qualities to batteries because its energy remains intact throughout storage periods.
3. Converting Hydrogen Back into Energy
An energy demand calls for hydrogen storage where the reserved hydrogen supplies the fuel cell or gas turbine to produce electricity. The complete process leads to only water vapor as a final output thus making it one of the cleanest power generation methods available.
Why Hydrogen Energy Storage Matters
Here’s why more governments and companies are turning to hydrogen storage:
✔ Long-Term Storage
Batteries are great for short bursts of energy storage. But hydrogen can store energy for weeks—or even months—without losing performance. It’s ideal for seasonal or backup power.
✔ Zero Emissions
When produced with renewable electricity, hydrogen emits no greenhouse gases. Its only output during energy conversion is clean water vapor.
✔ Versatile Applications
Hydrogen isn’t just for electricity. It can also:
- Fuel cars, trucks, and trains
- Power factories and industrial equipment
- Serve as emergency backup power for buildings and remote sites
Real-World Applications
Hydrogen energy storage is already making an impact in several key areas:
???? Industrial Use
The heavy power-consuming industries such as steelmaking and chemical production can substitute fossil fuels by using hydrogen.
???? Power Grid & Residential Use
Power utility companies employ hydrogen power storage to manage the power grid through energy distribution across times of high and low consumer demand.
???? Clean Transportation
Fuel cell vehicles enabled by hydrogen serve as an alternative fuel method that allows shorter recharging periods than electric vehicles and reaches further distances before needing more hydrogen.
The Challenges Ahead
While promising, hydrogen storage still faces a few hurdles:
- High Cost: Electrolyzers and storage tanks are expensive compared to battery systems.
- Limited Infrastructure: Hydrogen pipelines and refueling stations are still developing.
- Energy Loss: Converting electricity to hydrogen and back isn’t 100% efficient—some energy is lost along the way.
Global investment and technological progress are speeding up the development of better and cheaper hydrogen storage solutions despite the noted difficulties.
Looking Forward
Various countries including Japan and Germany together with the United States have started large-scale investments in developing hydrogen as part of their sustainable energy initiatives. The growth of demand for dependable renewable power sources has brought hydrogen energy storage into position to become a key stabilizing force for power grids and zero-emission advocate.
Final Thoughts
Hydrogen storage systems provide reliable storage of renewable energy through their clean and flexible operations. People who operate power grids as well as factory managers alongside casual observers of clean energy technology should consider hydrogen energy solutions as essential components for sustainable development.
Knowledge of these systems predefined our path toward developing an efficient environmentally-friendly energy storage system.








2 thoughts on “What Is a Hydrogen Energy Storage System and How Does It Work?”
Comments are closed.