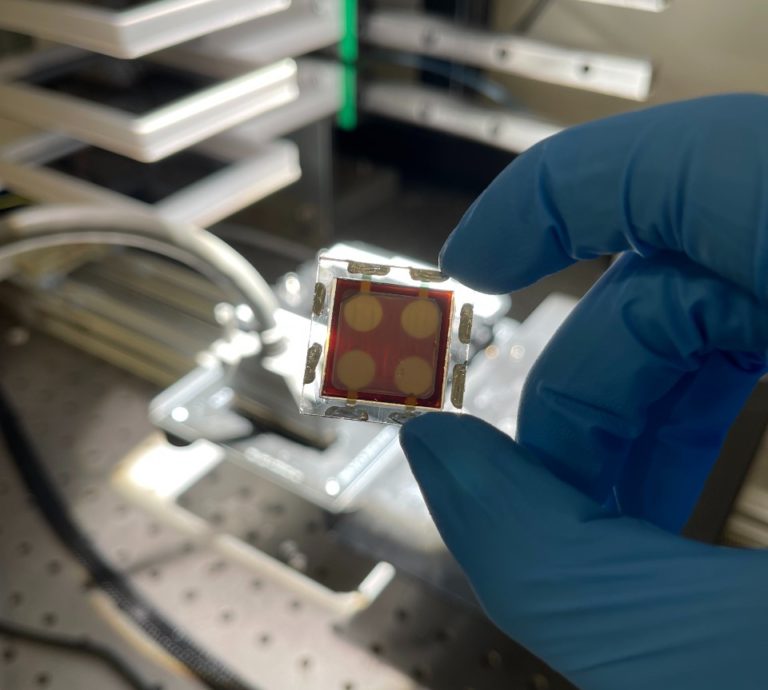
Controlling the crystallization technique of perovskite skinny movies is without doubt one of the most difficult features for upscaling photo voltaic tech, however an Australian analysis crew claims to have made a breakthrough by creating next-generation PV cells. which has the potential to rival the sturdiness of silicon alternate options.
from Australia’s pv journal
Researchers from the Australian Analysis Council (ARC) Middle of Excellence in Exciton Science, primarily based at Melbourne’s Monash College, say they’ve demonstrated a brand new method to make steady perovskite photo voltaic cells that last more than of their predecessors, to assist develop commercially related know-how. .
The manufacturing of perovskite cells typically depends on the usage of lead halides and requires the inclusion of robust solvents to manage the crystallization course of, a course of that may result in defects in skinny movies, which is able to trigger the ensuing system to quickly lose effectivity. It is usually troublesome to stop.
The researchers, together with colleagues from China’s Wuhan College of Know-how, stated the chemical compound lead acetate has emerged as a promising different precursor, as it could possibly produce ultra-smooth skinny movies with fewer defects. .
Till now, lead acetate has solely been used to make methylammonium or cesium-based perovskite, that are comparatively unstable and unsuitable for real-world functions. The analysis crew says that a greater candidate for industrial use seems in perovskites made with formamidinium and cesium, because of their superior stability.
Earlier makes an attempt to synthesize it utilizing lead acetate as a precursor failed however Dr Sebastian Fürer from Monash College stated to resolve this situation, the researchers used ammonium as a risky cation (positively charged which ion) at a important stage.
“The presence of ammonium serves to drive off residual acetate throughout annealing, with out forming undesirable facet merchandise,” he stated.
The researchers say that the cells recorded a conversion effectivity of 21%, the most effective outcomes recorded for a tool comprised of a non-halide lead supply. A mini prototype photo voltaic panel with cells achieved 18.8% effectivity.
Monash College PhD scholar Jie Zhao stated the take a look at units additionally confirmed robust thermal stability, persevering with to perform with out lack of effectivity after 3,300 hours operating at 65°C.
“We have been ready to make use of lead acetate in a one-step, spin-coating course of to acquire an ideal, high-quality formamidinium-caesium perovskite skinny movie,” he stated. “And since we do not want an anti-solvent agent, we will do it by way of large-scale strategies, like blade coating, which implies it may be finished on an industrial scale.”
The outcomes have been revealed in Power and Environmental Science.
One other crew of researchers from the ARC Middle of Excellence in Exciton Science has demonstrated a brand new method to enhance the steadiness of perovskite cells, resulting in thinner movies that they are saying are higher at high quality, with decreased defects and improved sturdiness.
The researchers stated that by eradicating the solvent dimethyl-sulfoxide and introducing dimethylammonium chloride as a crystallization agent, they have been in a position to higher management the intermediate levels of the perovskite crystallization course of.
The researchers, who labored with scientists from Oxford College in the UK, stated that teams of as much as 138 pattern units have been subjected to a speedy getting older and excessive temperature take a look at course of and actually world situations. The formamidinium-caesium perovskite cells made utilizing the brand new synthesis course of considerably outperformed the management group and confirmed resistance to thermal, humidity and lightweight degradation.
In the course of the take a look at, the most effective system operated above the T80 threshold for greater than 1,400 hours beneath simulated daylight at 65 C. T80 is the time required for a photo voltaic cell to scale back to 80% of its preliminary effectivity.
Over 1,600 hours, the management system manufactured utilizing the traditional dimethyl-sulfoxide method stopped working, whereas the units manufactured with the brand new, improved design retained 70% of their unique effectivity.
The identical degradation research was carried out in a bunch of units at 85 C, with new cells once more outperforming the management group.
The researchers estimate that the brand new cells age by an element of 1.7 for each 10 C enhance in temperature they’re uncovered to, which is near the two-fold enhance anticipated in industrial silicon units. .
Oxford College PhD scholar Philippe Holzhey stated the work, revealed in Supplies in Natureis a powerful step ahead in matching industrial silicon stability and makes perovskite-silicon tandem units a extra sensible candidate for changing into the dominant next-generation photo voltaic cell.
“It is actually vital that individuals begin shifting to comprehend that there isn’t any worth within the present if it isn’t a powerful present,” he stated. “If the system lasts a day or every week or one thing, there’s not a lot worth in it. It ought to final for years.”
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.