Researchers in South Korea have discovered that molybdenum ditelluride can improve provider technology in perovskite photo voltaic cells. They simulated a cell with a perovskite absorber and a layer made from the brand new materials, and decided that its effectivity may exceed 20%.
Researchers at Sungkyunkwan College (SKKU) simulated a tandem photo voltaic cell with two absorbers based mostly on methylammonium lead triiodide (CH3NH3PbI3) – a perovskite with excessive photoluminescence quantum yield – and molybdenum ditelluride (MoTe2), recognized for being naturally p-doped, with cascaded bandgaps to soak up a wider photo voltaic spectrum.
“The proposed cell configuration overcomes the present limitations of daylight absorption in perovskite photo voltaic cells,” stated researcher Mohammad Gholipoor. pv journale. “We expect this cell could possibly be one other new answer to alleviate this downside.”
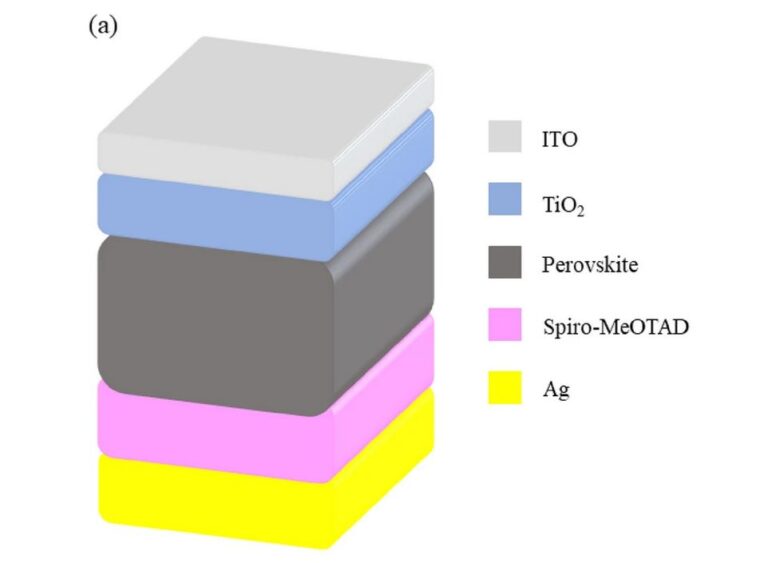
The scientists constructed the cell with the substrate indium tin oxide (ITI), a electron transport layer (ETL) based mostly on titanium oxide (TiO2), a CH3NH3PbI3 layer, a MoTe2 layers, a spiro-OMeTAD hole-blocking layer, and a silver (Ag) steel contact.
“The superb desired MoTe band alignment2 with different layers, with its excessive near-infrared (NIR) absorption capability, uniquely paves the way in which for reaching greater photovoltaic effectivity,” they defined, noting that the perfect which is the thickness of the MoTe2 The absorber ought to be about 25 nanometers.
They discovered that the CH3NH3PbI3 and MoTe2 The layers contribute 61% and 39% of the provider technology, respectively. They famous {that a} cell made on this configuration can attain an influence conversion effectivity of 20.32%.
“The calculated outcomes present a substantial improve within the perovskite photo voltaic cell effectivity arising from the brief circuit present, in comparison with the cell with out MoTe.2,” they stated.
Nevertheless, stacking absorbers with completely different bandgaps led to a lower within the open-circuit voltage, because of the degradation of the outlet transport within the absorbing space.
“To alleviate the inevitable situation, we inserted a layer of graphene oxide with a thickness of 1.5 nm. Due to this, we noticed that the voltage of the open circuit elevated as much as 0.1 eV,” they stated.
They offered a brand new cell design of “Excessive-performance parallel tandem MoTe2/perovskite photo voltaic cell based mostly on decreased graphene oxide as a gap transport layer,” which was lately revealed in Scientific experiences. They’re now attempting to get the experimental outcomes in step with their simulation outcomes.
“Qtransition-metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) reminiscent of MoTe2 it’s not very costly and may be simply ready by means of the exfoliation technique and development, in different phrases, the price of a cell will not be a difficulty right here,” defined Gholipoor. “Nevertheless, there are some technical and experimental points that should be resolved, reminiscent of the entire switch of MoTe2 flakes to the tough perovskite layer or excessive interlayer recombination of the 2 absorbers.”
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.