Passive solar module cooling tech based on water sorption – pv magazine International
South Korean scientists have developed a WD-ER cooling system that may decrease the working temperature of the PV panel as much as 14.9 C, with a median warmth switch coefficient of 64.1 W/m2.
A analysis group at Korea College has developed a passive cooling system for photo voltaic panels that makes use of a water desorption course of and an endothermic response dissolution course of.
The tactic is much like part change supplies (PCMs), which take in, retailer and launch a considerable amount of latent warmth in a selected temperature vary, and are sometimes used for cooling PV modules on the analysis degree. The system is cheap and doesn’t eat vitality, and it has self-healing properties, which make it very versatile.
“The proposed methodology has no vitality consumption and consists of low-cost supplies, which makes it very sensible,” the scientists declare. “Additionally, it may be used repeatedly, attributable to its self-recovery traits.”
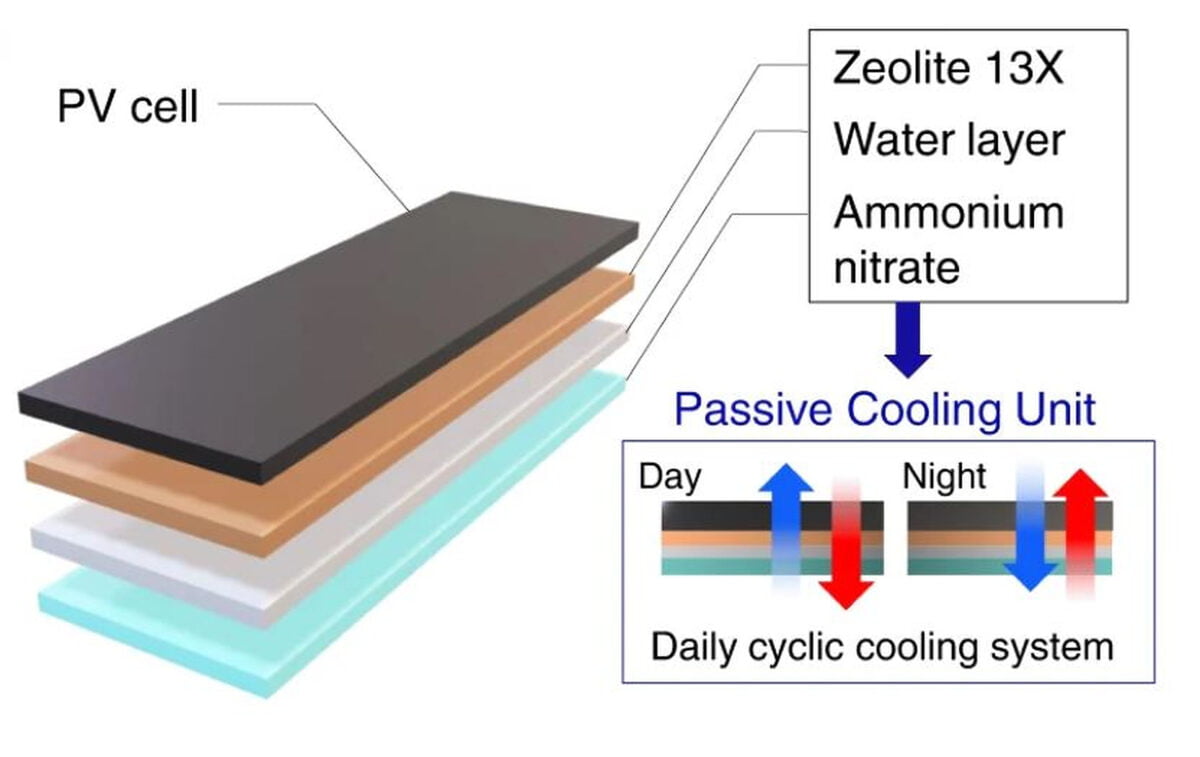
The researchers describe the approach as an atmospheric water desorption-driven cooling system that makes use of Zeolite 13X, a commercially obtainable alumino-silicate materials, to desorb water molecules producing a latent cooling impact. When warmth is utilized, water is desorbed from the Zeolite 13X and dissolves the ammonium nitrate (NxH4NO3) to induce an endothermic cooling response, leading to a reversible course of that recovers itself in a single day.
The water desorption-driven endothermic response (WD-ER) cooling system can take in warmth from photo voltaic radiation and desorb the solvent, producing secondary chilly vitality by dissolving the solute. The cooling impact is achieved as a result of the water adsorption capability of zeolite 13X is inversely proportional to temperature, and water can dissolve extra ammonium nitrate at greater temperatures.
The Korean crew hooked up the WD-ER system to the again of the photo voltaic cell with urethane waterproof to guard it from moisture. They coated the cell with Zeolite 13X particles and a small quantity of polyvinyl, then saturated these particles with water and added the NH4NO3 crystal layer to kind a skinny movie.
The WD-ER system has a median efficient warmth switch coefficient of 64.1 W/m2, and the thermal imaging taken at 2 pm exhibits that the floor temperature of the PV cell with the WD-ER cooling unit is 39 -43 C, which is vital. decrease than pure air cooling (51–56 C). The typical temperature of the PV cell with WD-ER is decreased by 14.9 C.
The researchers urged that this novel cooling system might outperform different cooling strategies reported within the literature, though they didn’t present an in depth evaluation of manufacturing prices or potential industrial purposes. .
They offered their findings in “Self-healing passive cooling utilizing the endothermic response of NH4not3/H2O pushed by water sorption for photovoltaic cell,” which was not too long ago printed in Communication in Nature.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and need to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: [email protected].